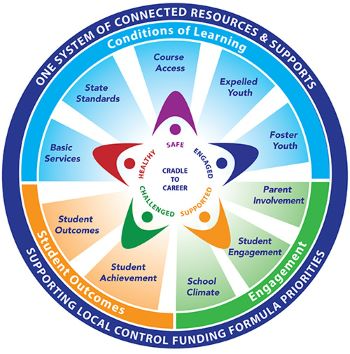
What is the purpose of the LCAP?
California's primary education finance law, the Local Control Funding Formula (LCFF), distributes base funding to districts based on student enrollment numbers. Additionally, districts receive supplementary funding per student to support the education of English language learners, foster youth, and economically disadvantaged students.
While districts have flexibility in allocating these funds, they are obligated to maintain transparency regarding expenditures, particularly for targeted student groups. The LCAP serves as the primary tool for districts to ensure this transparency. The State Board of Education provides districts with a standardized template organized around priority areas, which districts are expected to follow or customize to meet their specific needs. Enacted into law in 2014, the LCFF-LCAP system represents a significant legislative achievement during the Brown Administration.
Ensuring Accountability in School Districts
An underlying assumption regarding the LCAP is that community members will engage with it to hold schools accountable for achieving results and using additional funding appropriately. Originally created in 2014, the LCAP Parent Checklist, developed in partnership with the California State PTA, assists parents in understanding and providing informed input into the document.
Community Engagement
The LCAP process provides an opportunity for stakeholders to communicate their priorities to the district. It requires consultation with various groups, including the District Parent Advisory Committee (PAC), English Learner Parent Advisory Committees (DLAC), parents, students, school personnel, local bargaining units, and the community. School site councils and site-based student and parent groups (PTSAs) also play a crucial role in aligning their work with the district's LCAP.